The ENTIRE History of Human Civilizations: When Did Human Civilization Start?
Share your love
Introduction
Human civilization is a tapestry woven from countless threads of history, culture, and innovation. It’s a journey that spans millennia and encompasses a multitude of societies, each contributing to the rich tapestry of human development. In this article, we’ll embark on an exciting journey to explore the entire history of human civilizations, uncovering when and how it all began.
The Dawn of Civilization
When did human civilization start? To answer this question, we must journey back in time to the cradle of human civilization. Archaeological evidence suggests that the first inklings of civilization emerged around 10,000 BCE in regions known as the “Fertile Crescent.” This fertile land, located in present-day Iraq, Kuwait, and parts of Iran, was where humans transitioned from nomadic hunter-gatherers to settled agricultural communities.
The transition to agriculture marked a pivotal moment in human history. People began cultivating crops such as wheat and barley, and domesticating animals like sheep and goats. This shift allowed for the development of permanent settlements, the establishment of social hierarchies, and the birth of organized religion.
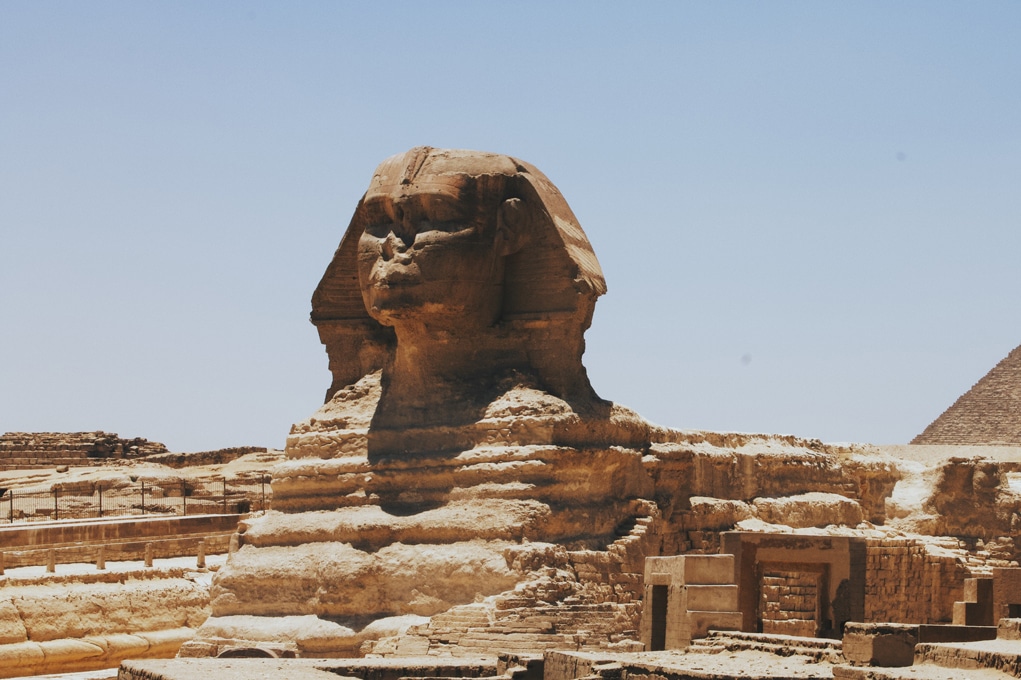
Mesopotamia: The Cradle of Civilization
One of the earliest and most iconic civilizations to emerge was Mesopotamia. Located in the Fertile Crescent, the ancient Mesopotamian civilizations, including Sumer, Akkad, and Babylon, laid the foundations for many aspects of modern society. They invented the first writing system, known as cuneiform, and created some of the world’s first legal codes, like the Code of Hammurabi.
Ancient Egypt: The Gift of the Nile
Around the same time as Mesopotamia, another great civilization was flourishing along the banks of the Nile River in Egypt. The ancient Egyptians left an indelible mark on history with their monumental architecture, hieroglyphic writing, and intricate belief systems, centered around the worship of numerous gods and the concept of an afterlife.
The Indus Valley Civilization: A Mystery Unearthed
In the Indian subcontinent, the Indus Valley Civilization thrived around 3300–1300 BCE. With its sophisticated urban planning, advanced drainage systems, and a script yet to be fully deciphered, this civilization remains a tantalizing enigma in our understanding of human history.
Ancient China: The Birthplace of Dynasties
Meanwhile, in East Asia, China was witnessing the emergence of the Xia and Shang dynasties. These ancient Chinese civilizations introduced innovations such as writing systems, the use of bronze, and an organized bureaucracy. Their legacies can still be seen in China’s rich cultural heritage.
The Greeks and the Birth of Democracy
The ancient Greeks are celebrated for their contributions to philosophy, science, and governance. In the 5th century BCE, Athens introduced the concept of democracy, a form of government that would profoundly influence the course of history.
The Roman Empire: An Empire of Unprecedented Scale
The Roman Empire, at its zenith, covered vast territories and left a lasting imprint on Western culture, law, and governance. With its mighty legions, magnificent architecture, and influential legal system, Rome’s influence extended far beyond its borders.
Medieval Europe and the Dark Ages
The fall of the Roman Empire marked the onset of the Dark Ages in Europe. During this period, various kingdoms and feudal systems emerged, and Europe underwent significant political and social transformations.
The Renaissance and the Age of Exploration
The Renaissance, which began in Italy in the 14th century, ushered in a period of renewed interest in the arts, sciences, and exploration. European powers embarked on ambitious voyages, leading to the discovery of new continents and the exchange of cultures between the Old World and the New World.
The Modern Era: Industrial Revolution to Globalization
The Industrial Revolution, which commenced in the late 18th century in Britain, radically transformed societies, ushering in an era of technological advancements, urbanization, and industrialization. The world has since experienced two World Wars, the Cold War, and the globalization of economies and information.
Conclusion
The history of human civilizations is an intricate tapestry woven together by countless cultures, innovations, and societal changes. From the dawn of agriculture to the modern age of globalization, the story of human civilization is one of resilience, progress, and adaptation. It is a testament to the limitless potential of human ingenuity and cooperation.
In our exploration of the entire history of human civilizations, we have uncovered when it all began—around 10,000 BCE in the Fertile Crescent. However, this is just the beginning of an ongoing journey, as civilizations continue to evolve and shape the world we live in today. As we reflect on the past, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable journey of humanity and the civilizations that have paved the way for our modern world.
References:
National Geographic Education: “Key Components of Civilization” Link
Read some more: How to Delete a Forked Repository in GitHub